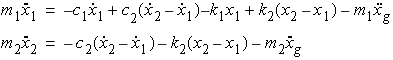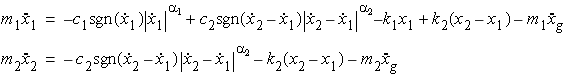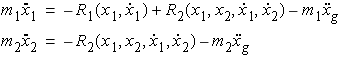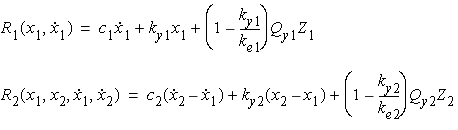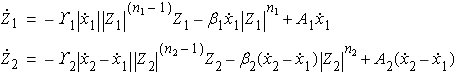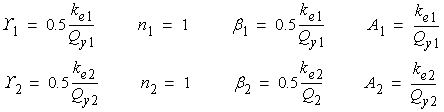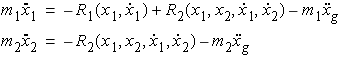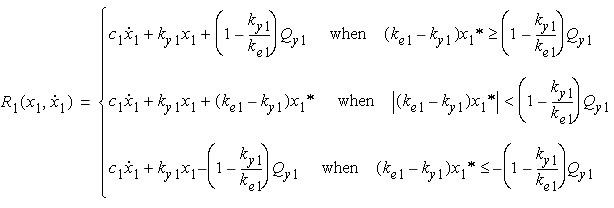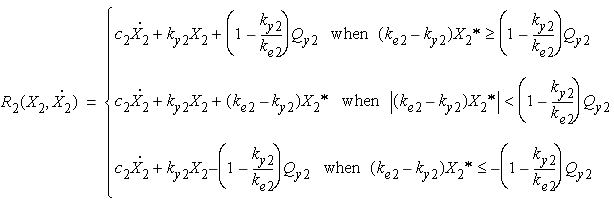|
Help Page
for the Java-Powered Simulation for Nonlinear
Two-Story Buildings |

|
Introduction
Welcome to the help page of the Java-Powered
Simulation for Nonlinear Two-Story Buildings.
It is common to
design structures to behave nonlinearly under extreme load conditions, e.g.
earthquakes and hurricanes. To instruct students or practitioners to better
understand the effect of nonlinear behavior of buildings, our research effort
has focused on the development of the nonlinear dynamic analysis virtual
laboratories.
In this simulation, the structure is modeled
as a two-story building. Same analytical model are used to described the
behavior of each story of the structure, while different parameters are allowed
for different stories. Based on different models employed, this simulator
consists of four cases: (i) linear structure with each story designed as linear
model; (ii) nonlinear structure with each story designed as nonlinear damping
model; (iii) nonlinear structure with each story designed as hysteretic bilinear
model; (iv) nonlinear structure with each story designed as hysteretic Bouc
Wen model.
The user is allowed to select different model
to design the structure, to change the parameters of the structure and choose
different earthquake ground motions to do analysis. This simulation is intended
to be used to increase understanding and provide a conceptual "feel"
for various parameter changes on the performance of nonlinear structures under
different excitations.
This document offers a description of how to
operate and use the Java-Powered Simulation for Nonlinear Structure, a picture
of which is shown below, and also the technical background of this simulation.
A number of "homework" problems (or exercises) are suggested and
references are provided.
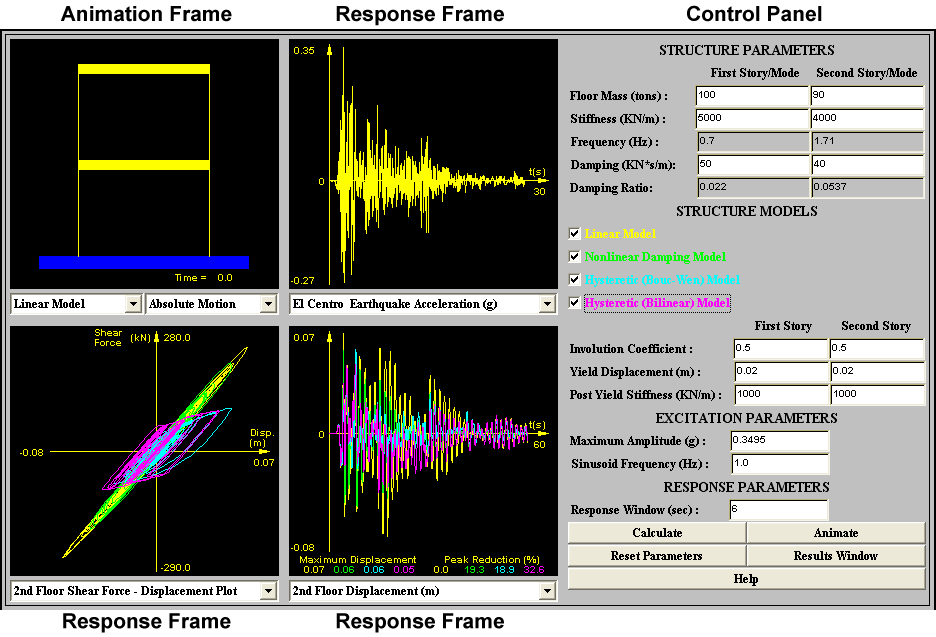
Fig. 1 Java-Powered Simulation Applet
How to Use
the Simulation
There are four components in this simulator
that can be modified by the user to design the structure and to evaluate the
responses: (1) Control Panel; (2) Animation Frame; (3) Excitation Frame; (4)
Response Frame. These are each identified on the above picture of the simulator.
Control Panel
Located on the far right of the simulator,
this panel is used to enter specific data for the structure and excitation.
This panel also contains buttons to do calculation and animation and the button
which links to this help page.
-
Floor Mass: The mass of the structure. The
default values are 100 tons for the first story and 90 tons for the
second story.
-
Stiffness: The stiffness of structure. The
default values are 5000 KN/m and 4000 KN/m for the first and second
story.
-
Natural Frequency: The natural frequency
of the structure. These parameters are not editable and they are determined
corresponding to other structure parameters.
-
Damping: The damping coefficient of the structure.
The default values are 30 KN*s/m for the first story and 10 KN*s/m for
the second story.
-
Damping Ratio: The damping ratio of the structure.
These parameters are not editable and they are determined corresponding
to other structure parameters.
-
Check Boxes: These check boxes allow user
to select different structure designs of which the response will be
displayed. The default is to display the response of the structure with
linear model for each story.
-
Involution Coefficients: The nonlinear damping
multiplier of nonlinear damping model. The default value is 0.5 for
each story.
-
Yield Displacement: The yield displacement
in each story for hysteretic models (Bouc Wen and Bilinear Model). The
default value is 0.02 m for each story.
-
Post Yield Stiffness: The post yield stiffness
in each story for hysteretic models (Bouc Wen and Bilinear Model). The
default value is 1000 KN/m for each story.
-
Maximum Amplitude: The maximum amplitude
of the earthquake acceleration. The default value is the same as the
original maximum acceleration of the earthquake excitation. By changing
the maximum acceleration of the earthquake excitation, one can compare
the responses of the earthquake records with different amplitude.
-
Sinusoid Frequency: The frequency of the
sinusoid excitation. The default value is 1.0 Hz.
-
Response Window: Width of the excitation/response
windows (in seconds) used during the animation. If you computer can't
display the animation smoothly, make this number smaller.
Animation Frame
The animation frame, located in the upper
left portion of the simulation window, shows the behavior of this two story
structure under the specified excitation.
Structures, designed as Linear Model, Nonlinear
Damping Model, Bouc Wen Model and Bilinear Model, can be animated by the
appropriate selection in the left choice of this frame.
The user can also choose to animate absolute or relative
motion of the structure:
-
Absolute Motion: Display the absolute motion
of the structure. Thus, the ground is seen moving.
-
Relative Motion: Display
the motion of the structure relative to the ground. Thus, the ground
is seen not moving.
Located in the top center of the simulator, the
excitation frame shows current excitation signal. Five historical excitation
records are available for simulation:
-
Sinusoidal Input: The default value of the
frequency is 1.0 Hz. The default value of the maximum acceleration is
0.3g.
-
El Centro Earthquake: North-south component
recorded at the Imperial Valley Irrigation District substation in El
Centro, California, during the Imperial Valley, California earthquake
of May 18, 1940. The magnitude is 7.1 and the maximum ground acceleration
is 0.3495g.
-
Tokachi-oki (Hachinohe) Earthquake: North-south
component recorded at Hachinohe City during the Tokachi-oki earthquake
of May 16, 1968. The magnitude is 7.9 and the maximum ground acceleration
is 0.2294g.
-
Northridge Earthquake: North-south component
recorded at Sylmar County Hospital parking lot in Sylmar, California,
during the Northridge, California earthquake of Jan. 17, 1994. The magnitude
is 6.8 and the maximum ground acceleration is 0.8428 g.
-
Hyogo-ken Nanbu (Kobe) Earthquake:
North-south component recorded at Kobe Japanese Meteorological Agency
(JMA) station during the Hyogo-ken Nanbu (Kobe) earthquake of Jan. 17,
1995. The magnitude is 7.2 and the maximum ground acceleration is 0.8337g.
The user can choose to display the displacement or the
acceleration signal of the excitation by proper selection of the menu.
Response Frame
There are two response frames, which are
located at the bottom left corner and bottom center of the simulator. These
two identical response frames facilitate the user to investigate the responses
of different stories or the same story at the same time. It can show the
displacement, velocity or acceleration of each story. It also can plot the
displacement (or velocity) vs. shear force (or damping force, or spring
force). Peak response information such as the maximum value of each response,
peak reduction (= maximum peak of each case / maximum peak of Linear Model
case * 100 (%)) is displayed in the bottom of this frame.
Definition of the Primary
Parameters
-
Mass of the first floor 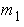 (kg)
(kg)
-
Mass of the second floor
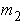 (kg)
(kg)
-
Stiffness of the first floor
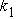 (KN/m)
(KN/m)
-
Stiffness of the second floor
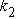 (KN/m)
(KN/m)
-
Damping coefficient of the first floor
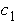 (KN*s/m)
(KN*s/m)
-
Damping coefficient of the second floor
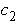 (KN*s/m)
(KN*s/m)
- For the cases of hysteretic model, the elastic stiffness
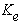 , post
yielding stiffness
, post
yielding stiffness
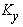 and yielding
force
and yielding
force 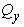 are defined as,
are defined as,
where
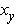 is the yield displacement (m).
is the yield displacement (m).
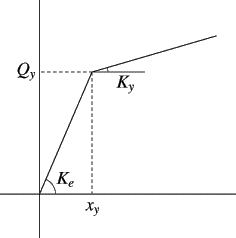
Fig. 2 Restoring Force vs. Displacement
The equations of motion for the structure with linear model
are
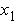 is the
first floor structural displacement relative to the ground (m).
is the
first floor structural displacement relative to the ground (m).
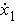 is the
first floor structural velocity relative to the ground (m/s).
is the
first floor structural velocity relative to the ground (m/s).
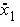 is the
first floor structural acceleration relative to the ground (m/s2).
is the
first floor structural acceleration relative to the ground (m/s2).
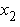 is the
second floor structural displacement relative to the ground (m).
is the
second floor structural displacement relative to the ground (m).
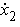 is the
second floor structural velocity relative to the ground (m/s).
is the
second floor structural velocity relative to the ground (m/s).
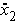 is the
second floor structural acceleration relative to the ground (m/s2).
is the
second floor structural acceleration relative to the ground (m/s2).
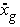 is the
ground acceleration (m/s2).
is the
ground acceleration (m/s2).
The equations of motion for the structure with nonlinear
damping model are
where,
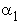 and
and 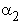 are the nonlinear damping
involution coefficients of the nonlinear damping model for the first and second
story, respectively.
are the nonlinear damping
involution coefficients of the nonlinear damping model for the first and second
story, respectively.
The equations of motion for the structure with hysteretic
Bouc Wen model are
where the restoring forces.
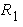 and
and 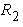 are defined as
are defined as
In the above equations,
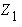 and
and 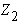 are the solutions of
the following equations,
are the solutions of
the following equations,
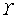 ,
,
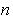 ,
, 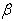 , and
, and
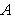 are the shape parameters for the hysteresis loops. In this case, these parameters
are defined here as
are the shape parameters for the hysteresis loops. In this case, these parameters
are defined here as
The equations of motion for the structure with hysteretic
bilinear model are
where the restoring forces.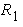 and
and 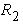 are defined as
are defined as
and
where
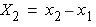 and
and 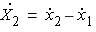 ;
;
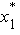 and
and 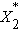 are displacements relative
to the center of the hysteresis loop.
are displacements relative
to the center of the hysteresis loop.
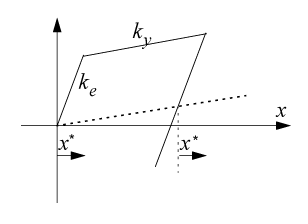
Fig. 3 Illustration of Displacement 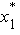 and
and 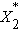
Spring Force: Force related to stiffness only.
Damping Force: Force related to damping only.
Shear Force: Summation of the shear and damping
force.
- Change the mass of the first and second floor; and then
calculate the response of the structure. Note that both natural frequency
and damping ratio are changed in this case.
Acknowledgements
The support of the National Science Foundation
under Grant No. CMS 95-28083 (Dr. S.C. Liu, program director), and the support
of the Multidisciplinary Center for Earthquake Engineering Research (MCEER)
are gratefully acknowledged. In addition, we would like to thank Prof. Yozo
Fujino of the University of Tokyo for his help in securing the Kobe and Hachinohe
earthquake records.